10 fascinating sea plants and interesting facts about them
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments. The sea contains thousands of plants essential to maintaining the marine ecosystem. Some of these sea plants are fascinating in their unique appearance and adaptations under water. They have complex colours and shapes. They are known for their extraordinary ability to survive underwater under low light depths.

Source: Getty Images
TABLE OF CONTENTS
The sea contains two categories of sea plants: some floating freely on water and others directly rooted on the ocean floor. These plants produce oxygen, shelter, and food for various marine life. Some sea plants are intriguing in many ways, such as appearance, shapes, and adaptations.
Fascinating sea plants
You will be surprised that marine plants, like terrestrial plants, also need sunlight for photosynthesis. That is why some aquatic plants are found floating on water. Below are some cool ocean plants, along with their pictures and fascinating facts.
1. Kelp
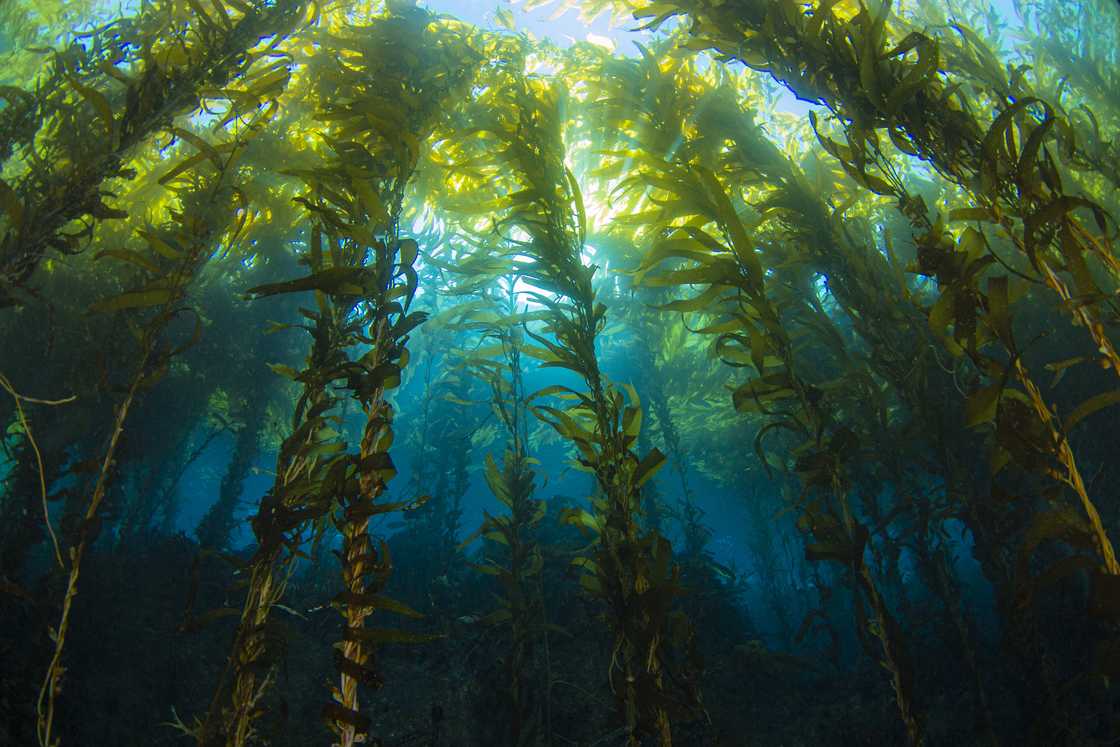

Source: Getty Images
Kelps are brown algae or seaweeds that live in relatively shallow, cool waters close to shore. They grow in underwater forests. Their bodies consist of leaf-like blades that originate from elongated stems.
Kelps are fast-growing marine plants. Some giant kelp can grow to 53 metres under suitable conditions; in ideal conditions, they grow up to 60 centimetres daily. Kelps provide a hiding place for many fish underwater and food for flattened sea snails called abalone.
Kelps have gas-filled bladders that help hold the blades closer to the ocean surface and thus the sun for photosynthesis. These sea marines do not have roots. They are secured by holdfasts that lock onto substrates made of rock or cobble under the sea. These holdfasts function like roots but do not absorb nutrients.
2. Seagrass
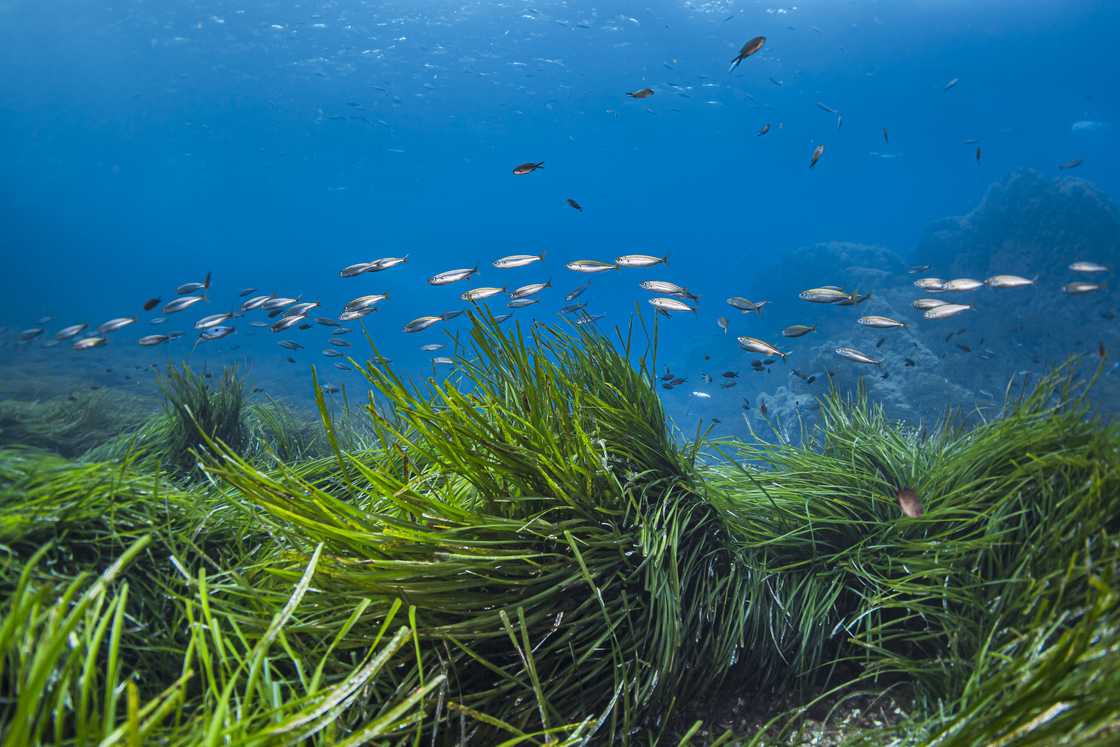

Source: Getty Images
Did you know that grass exists underwater, too? The sea also contains grass, which evolved from land plants and is one of the flowering plants in the ocean. Seagrass is similar to terrestrial plants in that it has flowers, leaves, seeds, roots, and connective tissues. Just like terrestrial grass, seagrass makes its food through photosynthesis.
Seagrass can grow as long as 7 centimetres. It is responsible for 15% of the ocean's total carbon absorption and provides shelter for a wide range of marine life, such as seahorses and juvenile commercial fish species.
Seagrass grow where sunlight is abundant because they need sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis. They enhance seawater clarity because of their ability to trap sediments and particles suspended in the water column.
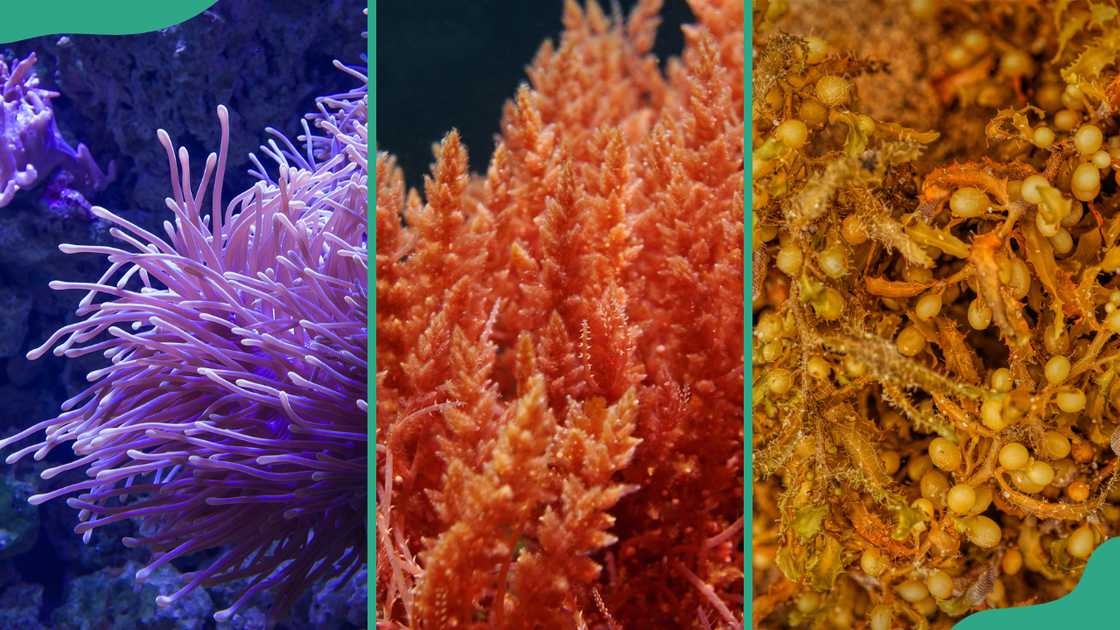
3. Red Algae
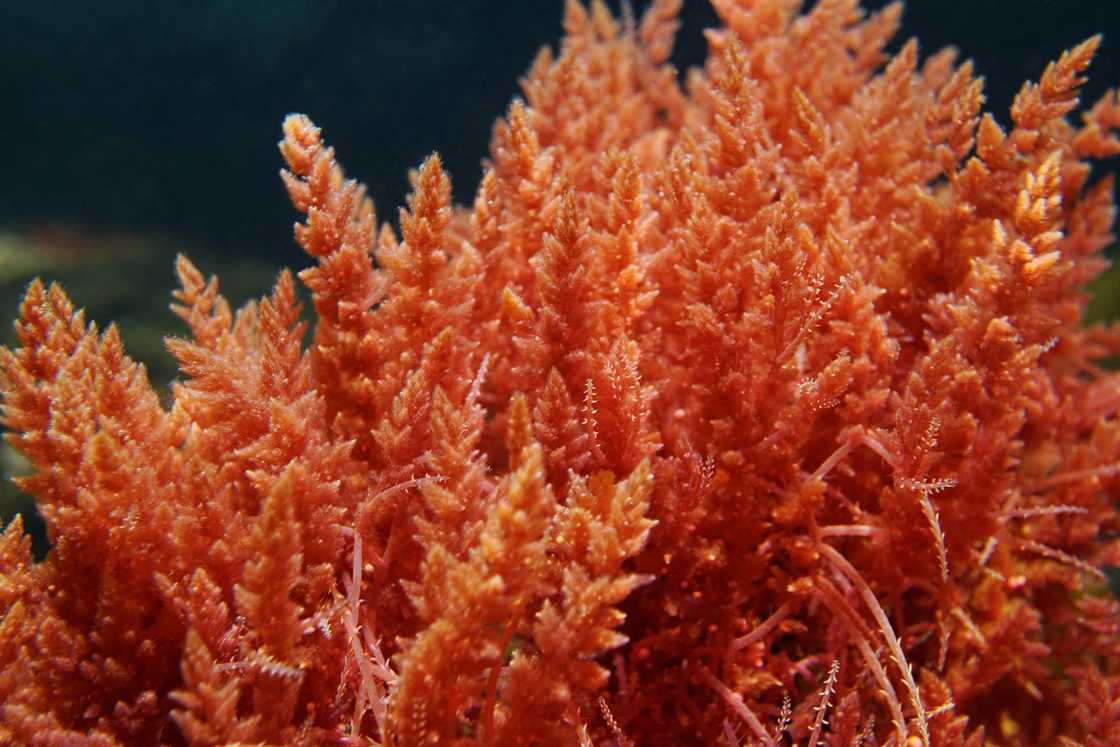

Source: Getty Images
The common algae, also known as Rhodophyta, is green, but did you know there are red algae in the sea? Red algae get their colour from the pigments phycoerythrin and phycocyanin, which mask other pigments such as chlorophyll a, beta-carotene, and xanthophylls. Like kelp, red algae is rich in proteins and vitamins.
Red algae is the oldest eukaryotic algae, containing over 600 species, and comprises some of Earth's oldest non-bacterial photosynthetic organisms. Unlike terrestrial plants, red algae do not have actual roots.
Red algae collect their nutrients through the 'skin' of their thallus. These marine plants are primarily found in deep water because they can absorb blue light and live more profoundly in the ocean, where light of long wavelengths cannot reach.
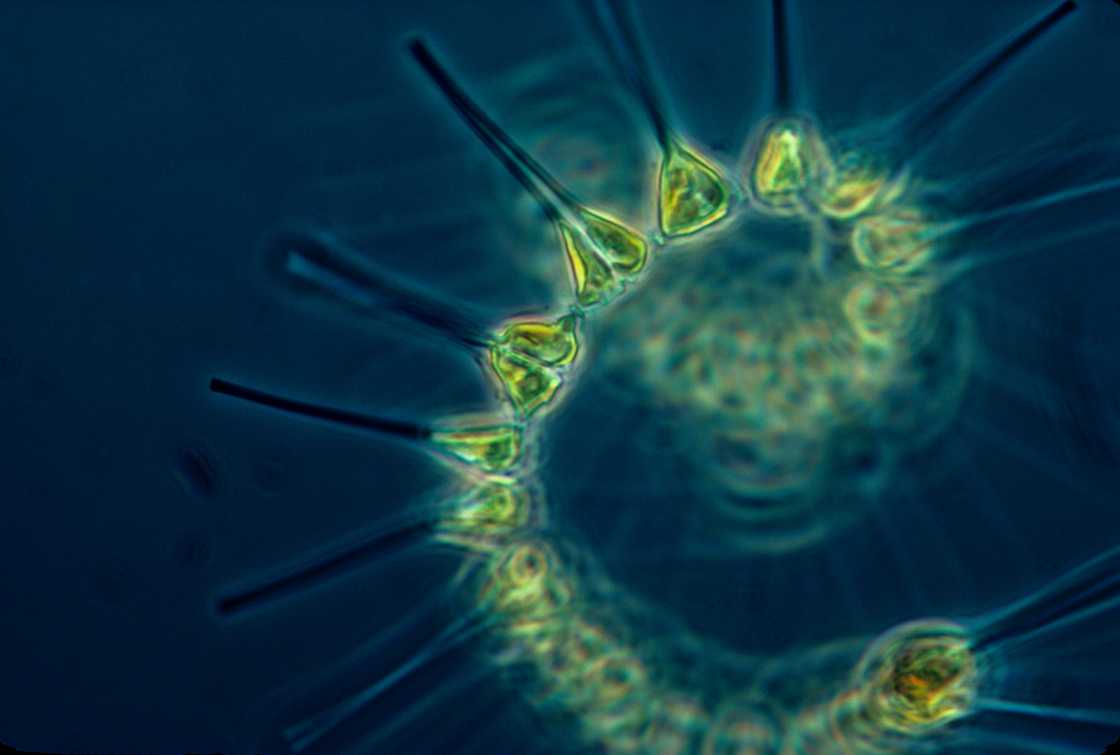
4. Phytoplankton
Source: Getty Images
Phytoplankton are microscopic sea plants that float near the surface water. They come in various shapes and appearances, others being spherical, elongated, spiral-shaped and forming chains or clusters. Most phytoplankton are green, but some are different colours, such as blue, yellow, brown, or red, depending on the pigment they contain.
Phytoplankton is a food source for many sea creatures, from the tiniest fish to the largest. As a microscopic organism, it is responsible for nearly 50% of the oxygen produced on Earth. It uses carbon dioxide from the water to make oxygen, which most living organisms, including humans, need to breathe.
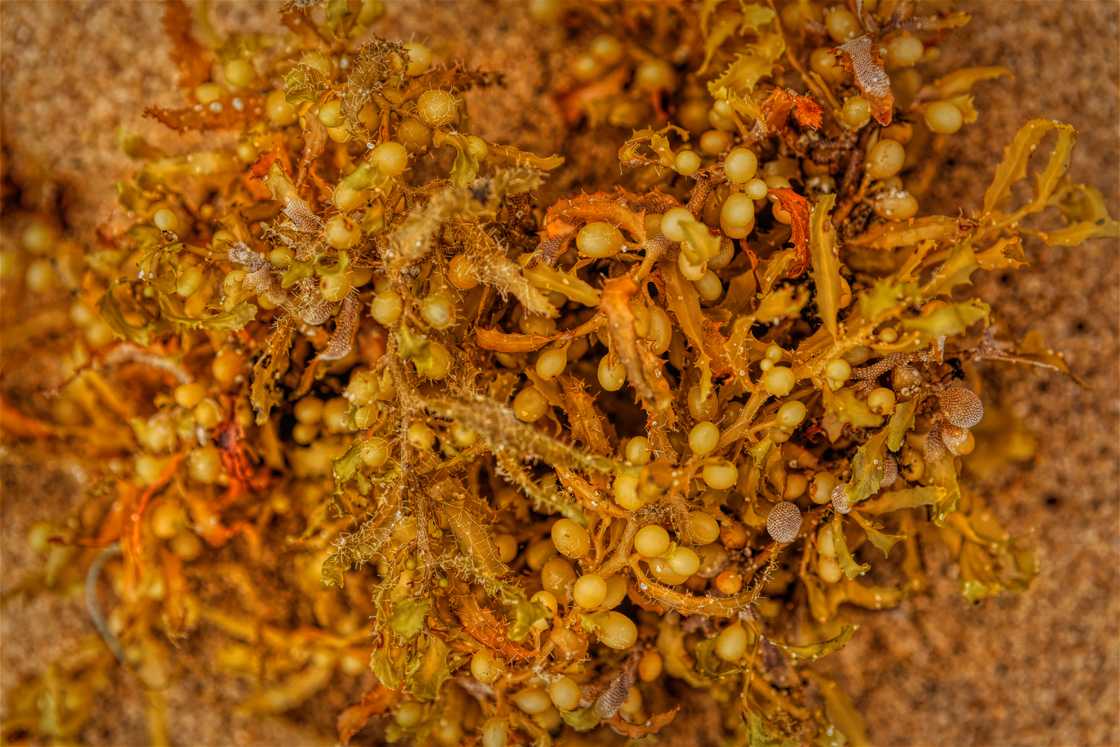
5. Sargassum

Source: Getty Images
Sargassum is a brown seaweed with berrylike bladders forming large floating masses. These marine plants float on water and never attach to the sea floor. They provide food, refuge, and breeding grounds for many aquatic animals, such as crabs, turtles, and shrimp. They can grow to a length of several metres.
Sargassum has berrylike gas-filled bladders that help the fronds to promote photosynthesis. They have a brown colouration. The bladder-floating nature keeps the plant floating up at the water's surface. Sargassum is found in tropical, temperate oceans, shallow waters, coral reefs, and the open ocean.
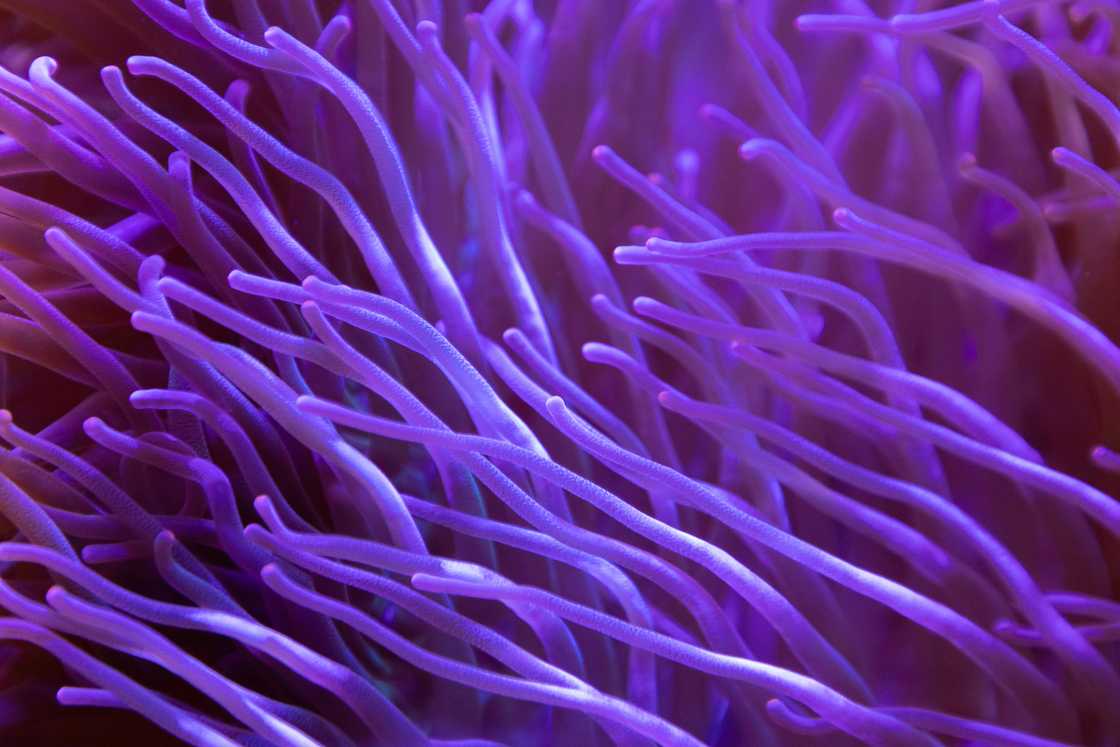
6. Purple coral

Source: Getty Images
One of the fascinating things about purple coral is its lilac colour. These marine plants get their colour from zooxanthellae, which give them nutrients. Millions of zooxanthellae are in the tissues of polyps. They grow in shallow waters, not deeper than 46 metres.
Purple corals are categorized as reef-building species. They can be found in both hard and soft forms. The hard corals contribute to reef building, while the soft ones provide homes for tiny and large fish and other marine life.
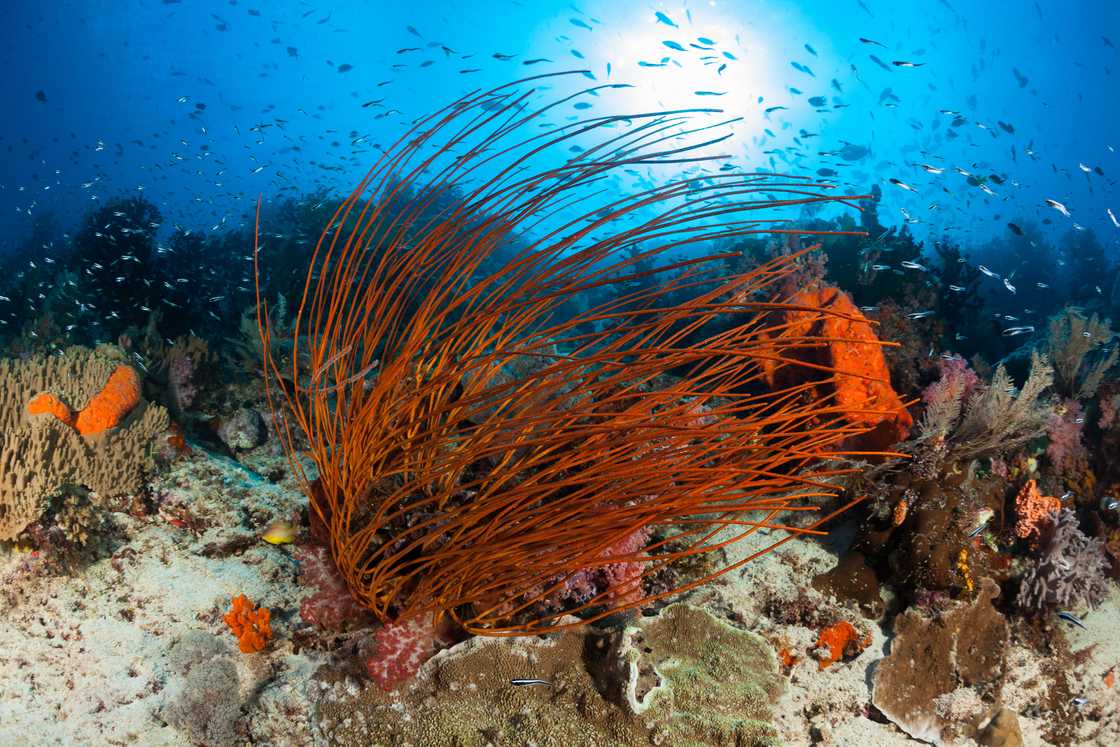
7. Red Sea Whip

Source: Getty Images
Red Sea Whip, also known as colourful sea whip, is a carnivorous species of soft coral. Its long, thin branches can grow to a metre long. The whips provide habitats for fish such as black sea fish.
The Red Sea Whip can grow up to three feet tall and displays various colours, such as yellow, orange, and deep purple. It has an internal axial skeleton, unlike true corals with rigid calcium carbonate skeletons.
Red Sea Whip is found in the Atlantic Ocean on various hard surfaces, such as rocks, bulkheads, and reefs. It primarily grows in shallow waters in the tropics and subtropics. The branches and stems of these marine plants are highly polished, and some species have been used as jewellery.
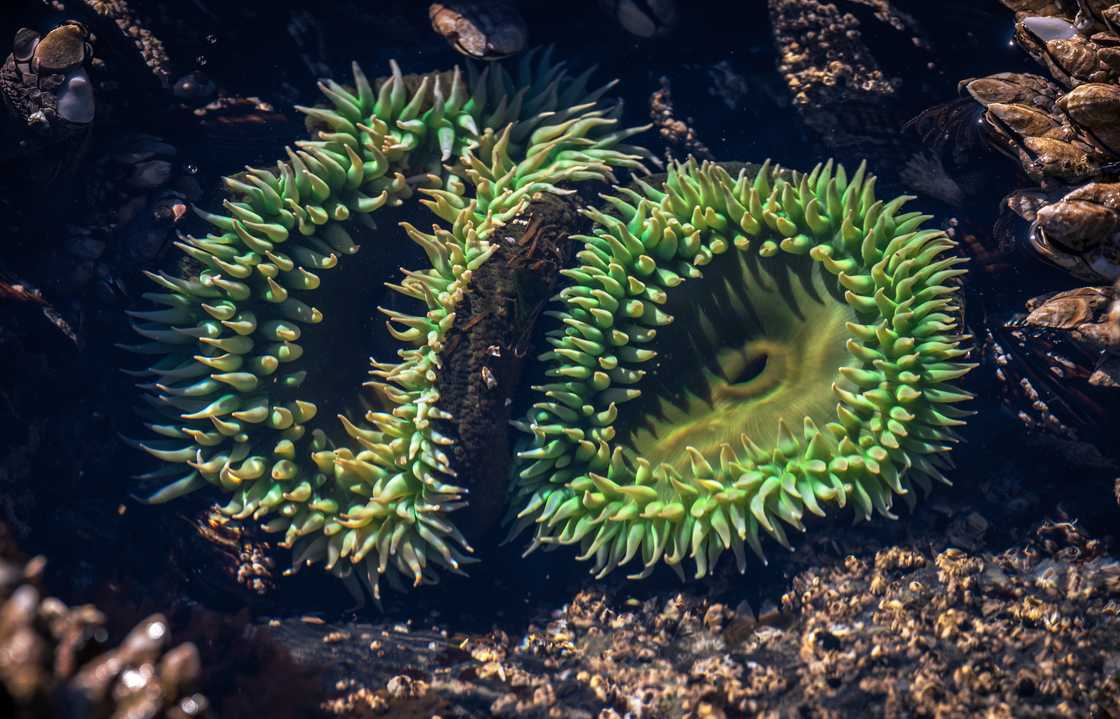
8. Giant Green Anemone

Source: Getty Images
Gian Green Anemone has a similar appearance to the terrestrial Anastacia flower. They are found in the intertidal and shallow subtidal zones along the Pacific coast of North America. The plant gets much of its colour through natural pigmentation; however, some is gained from the relationship between zooxanthellae and zoochlorellae.
Giant Green Anemones are carnivores that feed on dislodged mussels, crabs, small fish and sea urchins. They use stinging cells to paralyze their prey. These plants are used as a beneficial heart stimulant for humans. They change colour depending on how deep or shallow they are in water. When submerged, they appear bright green and green or brown when not submerged.
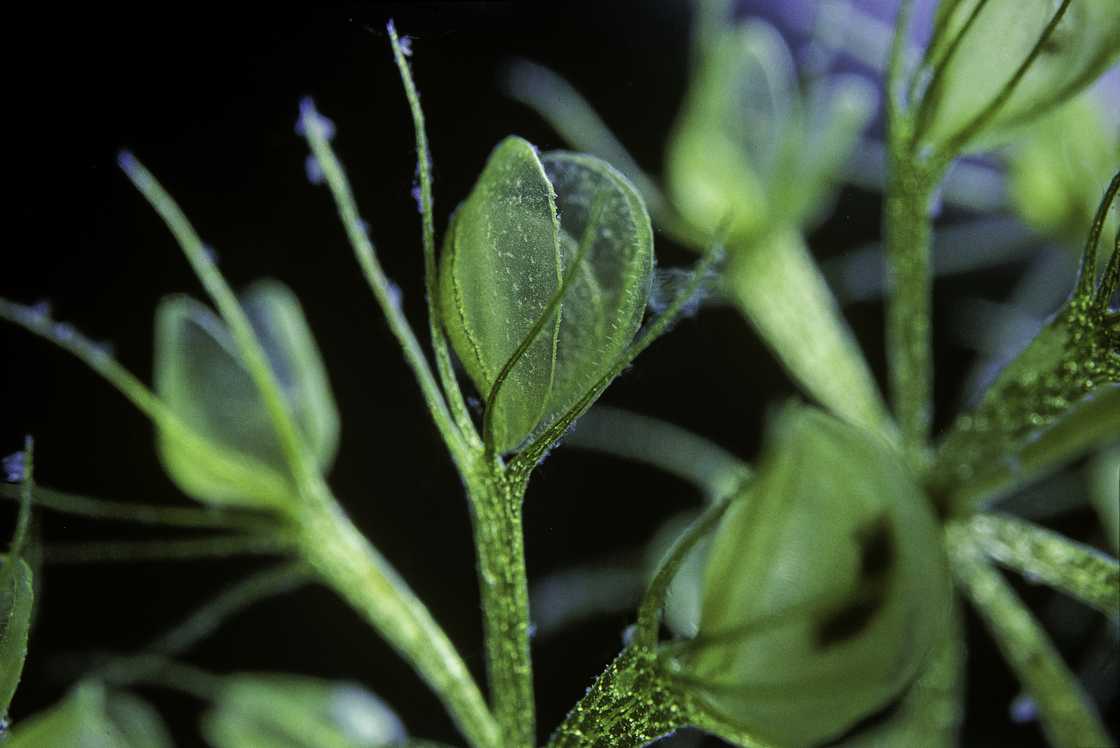
9. Waterwheel

Source: Getty Images
Waterwheel is a carnivore's sea plant that resembles the Venus flytrap. It captures small aquatic invertebrates using clamshell-type traps arranged in whorls around a central, free-floating stem. The plant is found below the surface of the water. Its floating stems can reach a length of 6-40 centimetres.
Waterwheels do not have roots, and they reproduce through vegetative reproduction. The most fascinating thing about this plant is that the only thing that pokes out of the water is the flower.
Waterwheels produce pretty flowers, which open for a few hours and are then drawn back to the water to produce seeds. The cotyledons remain with the seed coat to act as an energy source for the developing seeds.
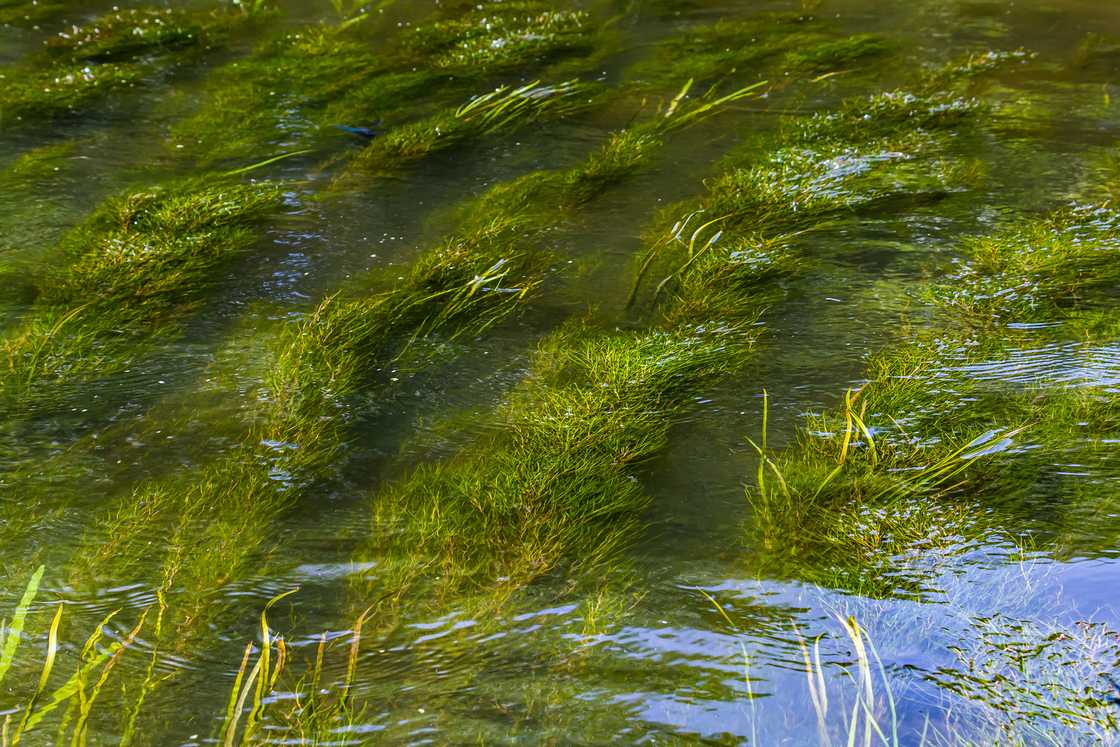
10. Pondweed

Source: Getty Images
Pondweed is also one of the fascinating deep-sea plants that grows in still or running water and sometimes has floating leaves. These plants are essential to the ecosystem because the structure created by pondweed shoots and leaves creates a habitat and shelter for aquatic insects and fish.
Pondweed grows in shallow freshwater lakes and floodplain wetlands. Its green roots are firmly underwater. These marine plants have modified rootlike stems and leaves of different shapes and sizes. The roots of these aquatic plants are not functional; they only provide support where the plant is anchored safely on the ground.
What are the most common plants in the ocean?
The most common plants in the ocean are Kelp, Sea Grass, Phytoplankton, and Sardines. These plants fall into three groups: euphotic (sunlight), disphotic (twilight), and aphotic (midnight). The group they belong to depends on how much sunlight they need to survive in water.
Are there underwater plants?
A large number of aquatic plants grow underwater. Some are entirely submerged underwater, while others have root systems at the bottom of the sea. Some of these plants include seagrass and broad-leaf pondweed.
What is the most popular plant in the ocean?
Phytoplankton is the most popular plant in the ocean. It floats on the water's surface and uses the sun's energy to procreate.
Most sea plants have striking appearances, colours, and shapes. They are an essential part of the marine ecosystem because they provide food, shelter, and breeding environments for aquatic life. Some marine plants include seagrass, Red Sea Whip, and Phytoplankton.

Source: Original
Legit.ng recently published a post on gorgeous exotic flowers globally that make lovely arrangements. Exotic flowers are an ideal intermediary when you cannot express a passionate statement in person.
Exotic flowers also add beauty and vitality to your environment. Some gorgeous exotic flowers include Birds of Paradise, Plumeria and Lily of the Valley. Find out more about exotic flowers in the article.
Source: Legit.ng








