Coronavirus: symptoms, transmission, possible treatment
All eyes are now glued to the outbreak of a disease caused by a novel coronavirus. The first case of this illness was registered back in 2019, attacking the city of Wuhan in China. Since that time, a range of Chinese cities have been put under travel restriction, but the pathogen has spread over to other countries. What do scientists already know about this disease and the level of danger it poses?

Source: UGC
There are hundreds of patients with a confirmed coronavirus diagnosis in China. It is supposed that the number of infected people can be much more, but some patients go unregistered, and others may still be in the incubation period. There are also cases registered outside China and in the United States.
What is coronavirus?
We are surrounded by pathogens of this family every day. Most people have already met them and got through the illnesses caused by them quite well. The family is extensive and includes several types that affect humans and animals like birds, cats, and dogs. If you look up the coronavirus definition on the internet or in medical reference books, you will see that some types of this pathogen migrated onto humans from animals like bats, palm civets, camels, and others.
Read also
24 hospitalised as strange illness emerges in Nigerian state, reportedly causing sudden collapse
As the coronavirus meaning suggests, they received their name due to the shape of their protein shell. It looks like a crown (‘corona’ in Latin) with protruding beams.
What is a coronavirus infection? Most commonly, it acts as a causative agent of respiratory infections and gastrointestinal disorders. The first time the pathogen was discovered in a laboratory was in 1965. Its carrier suffered from a heavy case of a running nose.
In humans, the most common coronavirus symptoms look like a common cold with a profusely running nose. Individuals with a healthy immune system would usually recover after several days of illness without complications. Children, older adults, and those with a compromised immune system, however, may develop bronchitis or pneumonia in a short while.

Source: UGC
Not all human coronavirus are as mild, though. There are two specific types known as SARS-CoV (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) and MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome). They are responsible for acute respiratory diseases that progress to pneumonia pretty fast. MERS is particularly deadly: 3 or 4 out of 10 patients with the confirmed MERS infection would die. Most of the fatal cases are connected to pre-existing health conditions that patients have before they get MERS.

Read also
LA wildfires: Chidi Mokeme shares devastating video of how his house in the US got burnt 5 years ago
People who already have cancer, HIV/AIDS, diabetes, lung, kidney, or heart issues are at a very high risk of not being able to survive MERS. This type keeps attacking humans from time to time, quite often, in the Arabian Peninsula. It is essential to inform doctors on one’s travel history and factual or alleged contacts with camels or any possible camel products to exclude or confirm the diagnosis of MERS after the manifestation of its symptoms.
Source: UGC
Unlike it, the SARS coronavirus has not been diagnosed in humans since 2004. It was primarily registered in 2002 in China. The severe outbreak of respiratory diseases caused by it spread over Hong Kong and Vietnam in two months then. In some more time, the illness was raging in other countries and on other continents. More than 8 thousand people had been infected, and about 8 hundred had died before the outbreak was stopped.
Symptoms of MERS include shortness of breath, fever, and coughing. SARS acts in a slightly different way. This coronavirus causes fever up to very high degrees, more than 38.0°C (100.4°F). It is accompanied by body aches, headaches, overall discomfort, and diarrhea at times. In several days, there comes a cough and, very often, pneumonia.
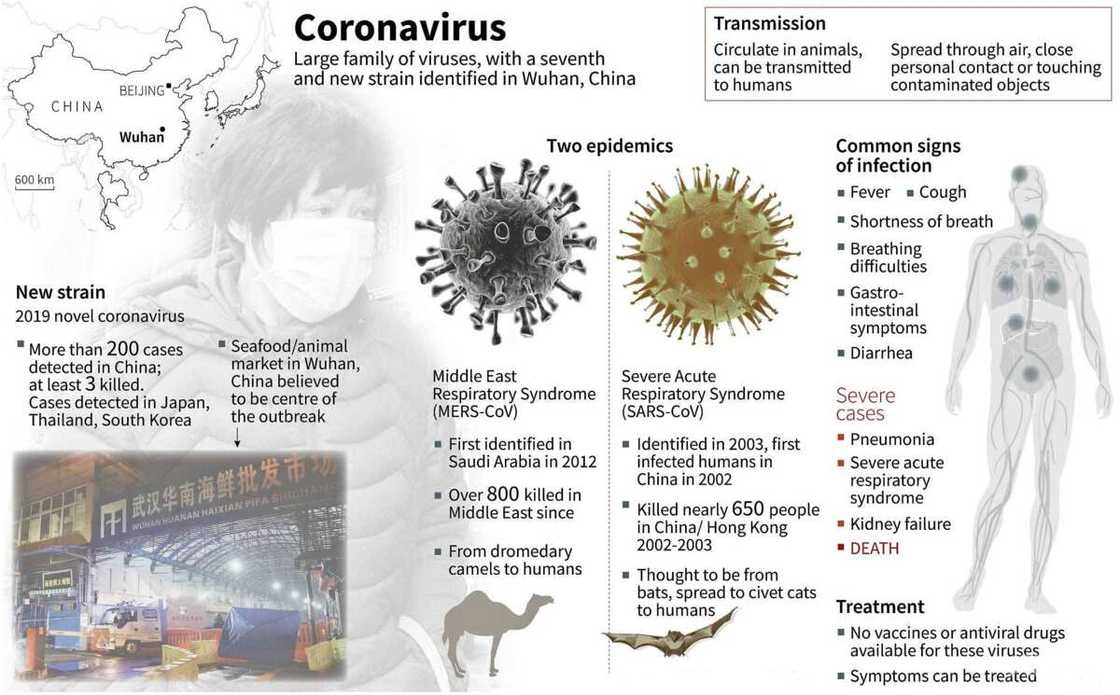
The novel coronavirus 2020 – what is it?

Source: UGC
Detected for the first time back in 2019 in Wuhan, the new disease was initially associated with the so-called wet markets. These are places where seafood and animals are being sold both alive and dead. This association suggested that the disease got spread to humans from animals.
When the number of patients started to grow, it became clear that many of them had not visited those markets before falling ill. At the moment, the novel coronavirus mode of transmission is under research. Experts suspect, though, that human-to-human transmission is in progress. It is still necessary to discover how quickly and easily an ill person can transmit the disease to others.
MERS and SARS often spread via droplets of fluids produced by ill people when they coughed or sneezed. This coronavirus transmission is the same as most respiratory diseases like flu or common cold types. Close contact between healthy and ill individuals helped MERS and SARS spread.

Source: UGC
It is still not known precisely how the 2019-nCoV (the name used for the new pathogen in compliance with the year of its first detection) is being spread. Though researchers suspect the same respiratory method, it is necessary to know for sure in order to develop more effective coronavirus prevention steps.
What are the new coronavirus symptoms in humans?
The symptoms resemble those of influenza. One may experience fever, shortness of breath, and coughing. The intensity may vary, and some people may have quite mild forms of the disease. The exact length of its incubation period is not yet known. Researchers believe that it may make something between 2 and 14 days after one’s exposure to the pathogen. They have come to this conclusion based on the experience of other viruses from this family.
What are the most effective coronavirus precautions?
Researchers will need to fill many blank spots when they get to know more about this novel pathogen type. Hopefully, they will find out how the disease is transmitted and how it can be stopped before it affects thousands of people on all continents. As of today, there is no coronavirus vaccine that would protect people from being infected or from developing complications.
Source: UGC
There is only a list of steps one can take to prevent the spreading of the pathogen, to protect themselves and other people.
- Wash your hands with soap thoroughly. It is necessary to use clean water and soap every time you wash your hands. The process should last no less than 20 seconds.
- Avoid touching your face if you cannot wash your hands. 2019-nCoV is supposed to get inside the body through the mucous lining. It is important not to touch your eyes, nose, or mouth if your hands are not freshly washed and wiped with a clean towel.
- By all means, avoid close contact with those people who already look ill, say they are sick, or have apparent symptoms. What do close contacts mean? If the disease is transmitted via droplets, it is necessary to stay away from the zone where they can reach you. Normally, the droplets do not fly further than 3 feet. Such is the recommended distance for talking to people. Also, close contacts include touching a person directly, hugs, kisses, sharing spoons, cups, plates and other utensils.
- Always cook eggs and meat very thoroughly.
If you develop the symptoms that feel like a cold, you also need to protect other people from possible infection.
- Stay at home and call the nearest hospital immediately. You should visit the hospital only after you get an appointed time for your visit. When making the appointment, explain your symptoms and tell them everything about your recent travels or communication with people who had suspicious symptoms, etc.
- Do not use fabric handkerchiefs. Instead, use paper towels and dispose of them every time you cover your nose and mouth while coughing or sneezing. After you get rid of the towels, wash your hands. If you are out of paper towels, cover your nose and mouth with your flexed elbow, not your hand. This will prevent spreading from your hands.
- Do not allow close contact with other people.
- If possible, clean all the objects or surfaces that can be contaminated with the pathogen. Use disinfectants in addition to washing.
If you have not traveled to China within a recent couple of weeks, then the symptoms will most likely indicate that you have a common cold or influenza. Nevertheless, you must be examined by a doctor to avoid complications.
Is there any effective coronavirus treatment?

Source: UGC
2019-nCoV has no specific therapy. There are no particular antiviral means that can help the body fight the pathogen quicker or easier. Until there is no diagnosed complications like pneumonia, only supportive care would help patients feel better and reduce the symptoms. It is crucial to monitor the condition of patients closely in case complications occur abruptly. Aggravated cases may require special means to support the vital functions of the body.
Each patient should be examined by doctors. Only prescribed care and means will be helpful. There is no need to use antibiotics until or unless they are prescribed. They do not kill viruses and thus are absolutely useless against them.
Researchers still need to discover more about the disease to develop a coronavirus cure that will get rid of the causative agent itself, not only its symptoms. Vaccines will also play a significant role if they are developed any time soon.
What is the situation with the novel coronavirus in the world today?
As of January 25, 2020, cases of the new disease have been registered in twelve states and territories outside China.
They are:
- Thailand (5 cases)
- Vietnam (2 cases)
- Singapore (3 cases)
- South Korea (1 case)
- USA (2 cases)
- France (2 cases)
- Japan (2 cases)
- Taiwan (1 case)
- Nepal (1 case)
- Pakistan (1 case)
- Australia (4 cases)
- Malaysia (3 cases)
Thirteen cities in China are already under travel restriction. The United States of America and France are the first to confirm cases of illness in Europe and overseas.
The World Health Organization has not yet declared a global emergency for the time being. Nevertheless, they are on high alert in case other countries also experience massive outbreaks or the disease shows its new and unexpected features.
The situation with the new coronavirus outbreak is under the closest surveillance of major health care organizations of the world. Governments of all countries have been warned and instructed on how to detect the disease and how to act in case of an emergency. Hopefully, the spread of the disease will be stopped effectively with all the experience scientists have from previous encounters with similar pathogens.
Source: Legit.ng