Health problems in Nigeria and their solutions
Nigeria, being one of the most developed African countries, is one of the worst states concerning health care rates. Tourists are scared to visit Nigeria to see its exotic beauty because they are afraid of being in extremes situation and be left without help. Read on to learn more about health problems in Nigeria and their solution.

Source: Getty Images
Healthcare in Nigeria
The healthcare in Nigeria has meager rates. The country has a mixed form of health care system, in which the public and private sectors of medical care are combined. The main range of qualified medical services is concentrated in private medical institutions. The primary health care in Nigeria is provided by public hospitals. They even have resuscitation units and can be found only in large institutions located in resort areas or large cities.
Medical personnel is trained in the medical faculties of the University of Ibadan in Nigeria, schools in Zaria and Lagos, and the cities of Kano and Sokoto. In general, there is no shortage of medical establishments in Nigeria — there are even schools for the training of midwives and nurses, a medical faculty, medical schools, two university faculties for laboratory technology, and a dental school. However, it does not entirely provide the country with qualified medical personnel, because the most promising doctors leave Nigeria.
It should be said that the problem of the quality of service in Nigeria is one of the most acute health challenges in Nigeria. The prices at the private medical institutions are too high for the average citizen, and the services provided there hardly correspond to their cost.

Source: Getty Images
Personnel working in Nigerian clinics do not always have the appropriate qualifications, and therefore are unable to provide people with essential and proper medical care. They are also poorly paid, and that is why they lack empathy. Besides, there is also a lack of medical facilities, medical tools, funding, and medications. Moreover one can observe corruption in the health care sphere.
The main number of highly specialized clinics and hospitals is concentrated in the capital of Nigeria. Here you can find a specialist of almost any profile and get the maximum possible list of medical services for the country, which includes diagnosis and treatment, x-rays and ultrasound, as well as a number of simple operations.
In 1970, the average life expectancy for men was 37.2 years, and for women - 36.7. By 2011, these figures increased for women to 55.3, for men to 48.9, that indicates an improvement in the quality of life and medical care. Current life expectancy in Nigeria according to www.vanguardngr.com is 54.07 years. The country’s life expectancy is ranked 216th in the world, and 16th in Africa. For comparison, in China and Japan average life expectancy is 83-84 years, and in European countries like Switzerland, Iceland and Spain – 82 years.
READ ALSO: List of social problems in Nigeria
Сurrent health issues in Nigeria
- There is a very high risk of infectious and parasitic diseases, including bacterial diarrhea, typhoid fever, hepatitis A, yellow fever, malaria, and meningitis in Nigeria. Malaria in Nigeria has a particular distribution and is found everywhere. The matter is in the high intensity of its transmission, due to which, despite the prevention, more than 15% of newcomers fall ill.
- A hereditary disease called sickle cell anemia is common among the black skinned population. Nigeria has the highest burden of Sickle Cell Disease, and according to www.premiumtimesng.com, over 150,000 children die from it every year.
- Water is often dirty in Nigeria. The establishments for cleaning water are poorly sponsored, and the quality of water is also reduced. This causes diseases. The primary cause of outbreaks of enteric-infectious diseases is polluted water since only 57% of the population has permanent access to clean drinking water. The lack of clean drinking water is one of the challenges in Nigeria. In October 2005, cholera outbreaks were recorded in the northeastern areas. It resulted in the death of 26 people.
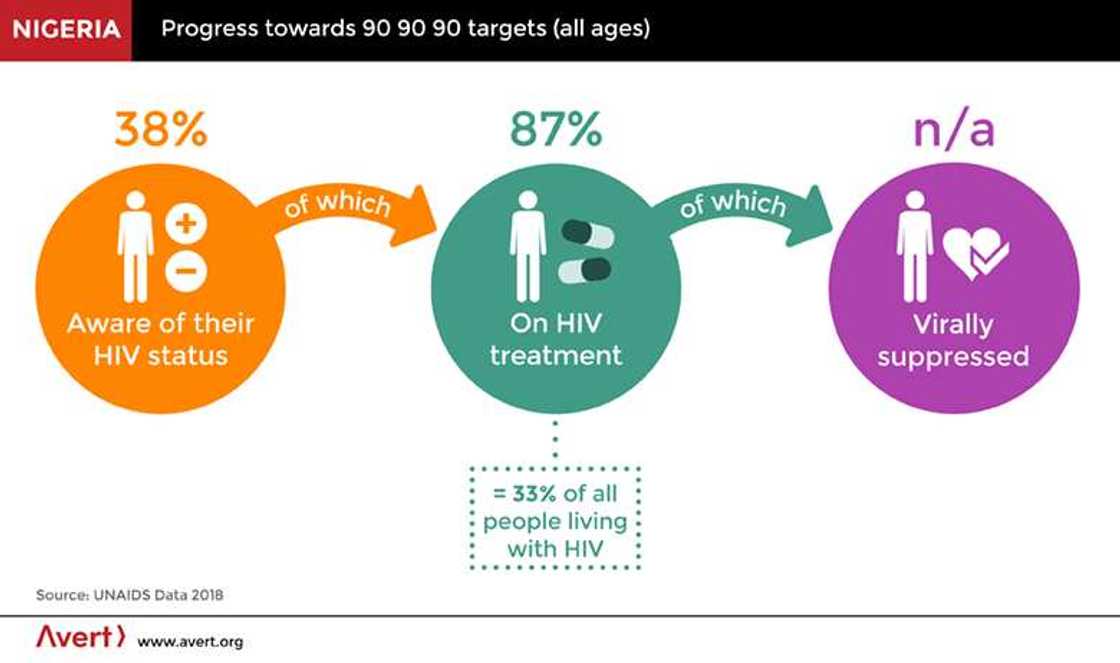
- A special problem of Nigerian health care is AIDS. Nigeria belongs to the top ten countries in the world with the most significant number of people infected with AIDS. In 2003, there were 3.6 million HIV-infected and AIDS patients, 310 thousand people died. According to www.avert.org, 3,5 million HIV-infected people currently live in Nigeria. One hundred fifty thousand people died from AIDS in Nigeria in 2017, and only about 33% of infected people receive any treatment. From the beginning of the 2000s, actions to implement the national program to combat AIDS intensified.
Source: Getty Images
READ ALSO: 10 best HMO in Nigeria
Moreover, there are health issues connected with the following factors:
- It is very dirty on the streets of the country. There is a lot of garbage in the state and poverty also presents an adverse effect on the conditions on the roads.
- Interruptions in light and water supply. In many homes regularly occur disruption in the supply of electricity and water. Some residents acquire autonomous electric generators. In the huts of the poor people there is no electricity at all, and water supply too.
- Horrible medicine. As you have already understood from the information provided to you above. In Nigeria, it's better not to get sick. The country has a poorly developed health care system. More or less decent medical care can only be obtained in paid private clinics that are inaccessible to the average population of the country. There the level of medicine is much lower than in Europe.
- Unemployment. Unemployment in the country causes poverty. Moreover, people have to look for the income illegally. Sometimes children are engaged in illegal trade from a young age. They trade with forbidden substances that cause addiction and other illegal stuff. Some people beg. But those who have a job, often suffer from terrible work conditions.
- Poverty. Although Nigeria is rich in oil, gold, and other minerals, it does not affect the well-being of many citizens. More than 67% of citizens live below the poverty line. The so-called middle class is only 3% of the total population, and there are even fewer wealthy people among Nigerians. The range of criminal activity is also caused by poverty.

Source: Getty Images
READ ALSO: Primary health care in Nigeria - challenges
- Armed conflicts. The last armed conflicts were in Nigeria in 1998, 2006, 2009 and 2016. Armed conflicts cause the crisis. Many refugee women lost their homes as a result of armed conflicts. In Nigeria, internal political and religious conflicts occasionally flare up from time to time. In some areas of the country, there are terrorist groups. In 2015, a terrorist group destroyed 16 villages and cities in the north of the country. At any time, a Nigerian citizen may lose their homes and become a refugee. It also causes poverty, unsanitary conditions, and diseases.
- Floods that take lives and destroy many homes. Because of climate changes on the continent, in Nigeria, as in other African countries, natural disasters often occur. In addition to the drought, sudden floods occur here. They take dozens of lives and destroy hundreds of homes causing adverse unsanitary conditions and dirtiness on the streets.
- Heat periods. It is boiling in Nigeria. The situation with the lack of water becomes critical when people fail to follow the rules of hygiene.
Source: Getty Images
There are several possible solutions, of course. Despite the fact that the most significant changes depend on the government and the head of the state, you can personally do the following:
- educate yourself as much as it possible;
- become a student of local or international health care establishment;
- work in your country and do not leave it;
- involve yourself into charity;
- become a volunteer to help those who live in poverty;
- visit meetings against indifferent authorities;
- mind contraception;
- write to the international European communities to draw attention to the problem of healthcare in your country.
As it can be observed there are severe problems in the sphere of health care in Nigeria. Besides the reformation must take place not only in the field of medicine but also in other areas that are connected and inevitably interact with health care. It means, that despite severe reforms in the medicine the poverty will, in any case, lead to the wide spread of infectious diseases and bad education will lead to the low consciousness of the society that may cause the unprotected contacts between individuals and the spread of, for example, AIDS. Unfortunately, people have nothing to do with this and the only way out is to wait for the further actions from the government.
READ ALSO: 5 Health Blogs in Nigeria You Need to Visit
Source: Legit.ng







