How to calculate company income tax in Nigeria
You want to build a company, but have no idea about company income tax? Then you need to start with the basics! What you are looking for, in terms of your company, is the corporate income tax. Fortunately, the laws of the country provide different options for owners of the companies! Take a look at how much you need to pay to the government according to laws!

Explanation of Corporate Income Tax
The resident companies of Nigeria are eligible to provide the liable to corporate income tax based on their worldwide income. At the same time, non-residents are only eligible to provide the taxes based on their Nigerian ventures.

READ ALSO: What is withholding tax in Nigeria?
The company income tax in Nigeria is 30%. It’s assessed on a preceding year basis. What does it mean? It means that the profit is charged on profits for the accounting year, but in the year which precedes the assessment.
All the non-resident companies in Nigeria are privileged to have a permanent establishment or fixed base in the country. These attributes are taxable on fixed rates. It’s necessary to register them for company income tax and file its tax returns. By the way, if you are interested in the history of taxation, then you will need to read this article!
FIRS company tax
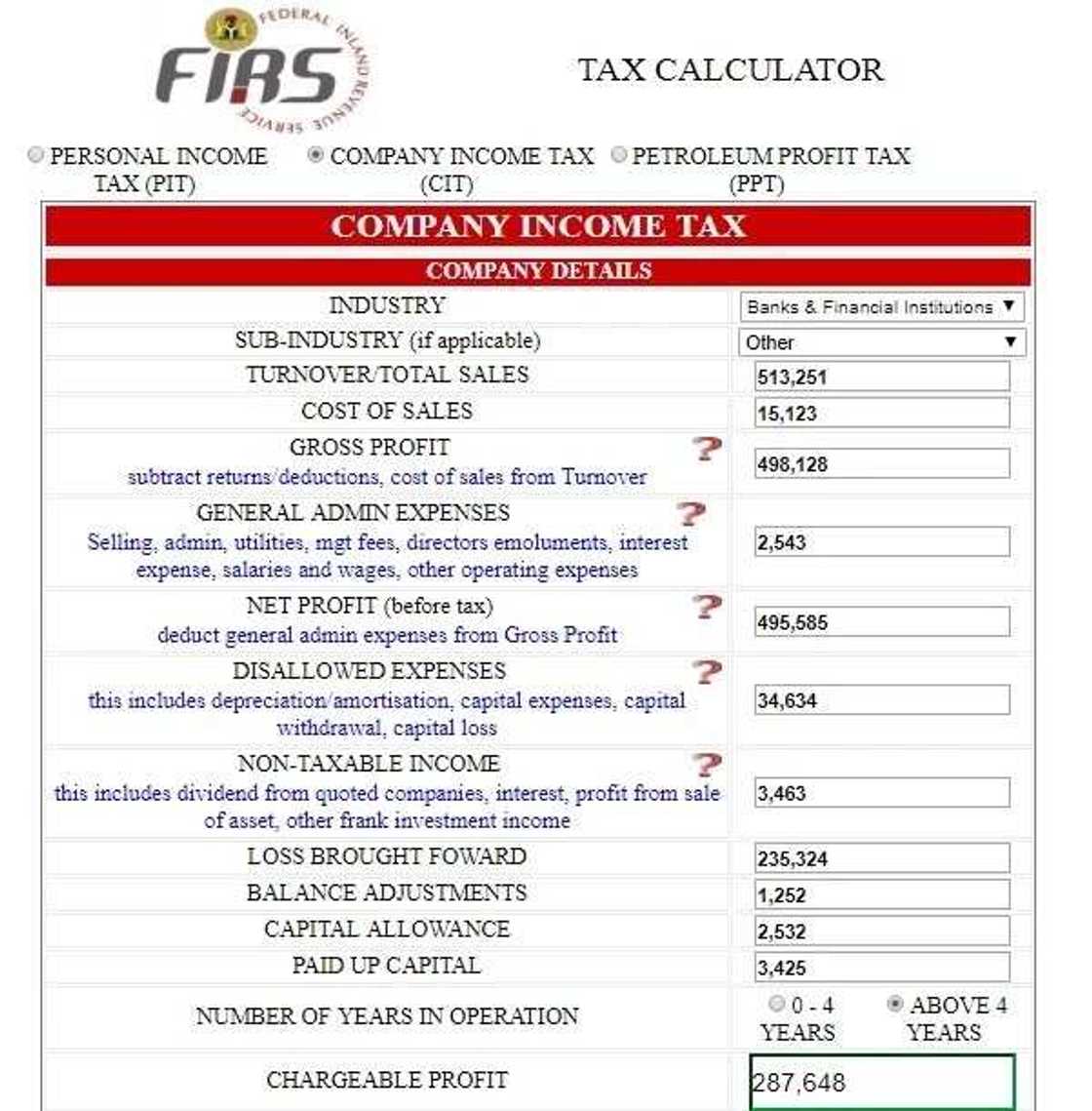
The main body that collects taxes in Nigeria is FIRS. This service even created the tax calculator for corporations in Nigeria. If you don’t have a tax manager in your company, who can calculate the income tax for you, then you may need to get your hands on this calculator. Let’s take a look at it!
- Industry - The first thing that you need to provide according to the calculator is the industry where you operate your business.
- Sub-Industry – It’s another thing that you need to include in your taxes. There are different income tax rate calculations for different industries.
- The turnover or Total Sales – it’s pretty simple. You just need to calculate the total sales of your production.
- Cost of Sales – It means how much you pay to provide the sale. For instance, it can be the price of materials, promotions, transportation and so on.
- Gross Profit – It’s total sales minus cost of sales. That’s the real reason for any business existing.
- General Administration Expenses – It’s the cost of everything connected with the expenses of your business administration. It includes operating expenses, wages, and salaries, interest expenses, directors’ emoluments, MGT fees, utilities, administration, and sales.
- Net Profit – it’s the profit before tax. You just need to deduct general administration expenses from the gross profit, and you get the number.
- Non-Taxable income – It includes various positions, like, frank investment income, profit from the assets, interest, dividends from the quoted companies and so on.
- Loss Brought Forward – it’s a provision that allows to carry over tax loss to future years of business. It’s needed to reduce future tax payments.
- Adjusted Balance – It’s based on the finance charges of the amount owed at the end of the billing cycle. It’s necessary for the calculation of all saving accounts.
- Capital Allowances – they are available according to the respect of qualifying capital expenditure and based on the assets which are used for a rental business or trade. It helps to write off the cost of assets for a certain period of time.
- Paid Up Capital – it’s considered to be the amount of money which the company gets from the shareholders. It’s the pay for holding the share stock.
- Number of Years in Operation – It’s quite easy, you just need to include the number of years that you work in the business.
When you get all data correctly, you can expect to get the Chargeable Profit, Company Income Tax, Education Tax and The Levy for Information Technology Development.
Small Company Rates

READ ALSO: Where are the NGOs in Nigeria that can give out loans without collateral?
If you deal with the small company, then you can expect deduction of taxes. In this case, the company income tax can be reduced to 20%. At the same time, the company must follow certain requirements to get this tax.
This deduction in taxes is provided for companies which turnovers do not exceed one million Naira. At the same time, these companies should work in the wholly export-oriented industry or manufacturing.
If you need to calculate your Personal Income Tax in Nigeria, then you can take a look here!
Minimum Tax

There is also the minimum tax paid by companies which can’t provide the turnover of more than five hundred thousand Naira. For these companies, there are special tax rates:
- Gross profit rate – 0.5%
- Net assets rate – 0.5%
- Paid up capital rate – 0.25%
- Turnover rate – 0.25%
If the turnover is higher than five hundred thousand Naira, it’s needed to add 0.125% on the turnover excesses.
The minimum tax is paid by companies with no taxable profits. Moreover, the tax on profit should be below the minimum tax. At the same time, the companies who are engaged in the agricultural business and other companies with at least 25% of the foreign equity capital are exempt from this tax.
Local Income Tax

Do not forget that corporate income tax is paid to the Federal Government of Nigeria. There are also local taxes which are different for every state in the country. Do not forget to check them also, if you want to open any business in Nigeria.

Company tax rates may seem complex, but if you invest enough efforts into this topic you can figure it out! You just need to know your numbers and then put them together for tax collection. That’s all that you need to know!
READ ALSO: Tax system in Nigeria: issues and challenges
Source: Legit.ng





