Igbo alphabet and pronunciation
Igbo is an African language that is part of the Congo-Kordofan family group. Igbo alphabet is quite easy to learn and remember as it is based on Latin letters. Today more than 30 million people who speak Igbo. The language is distributed in the south-eastern regions of Nigeria and has more than 20 dialects, including Ekpeye, Owerri, Ika, Ida, Aro, Ogu, Uku.
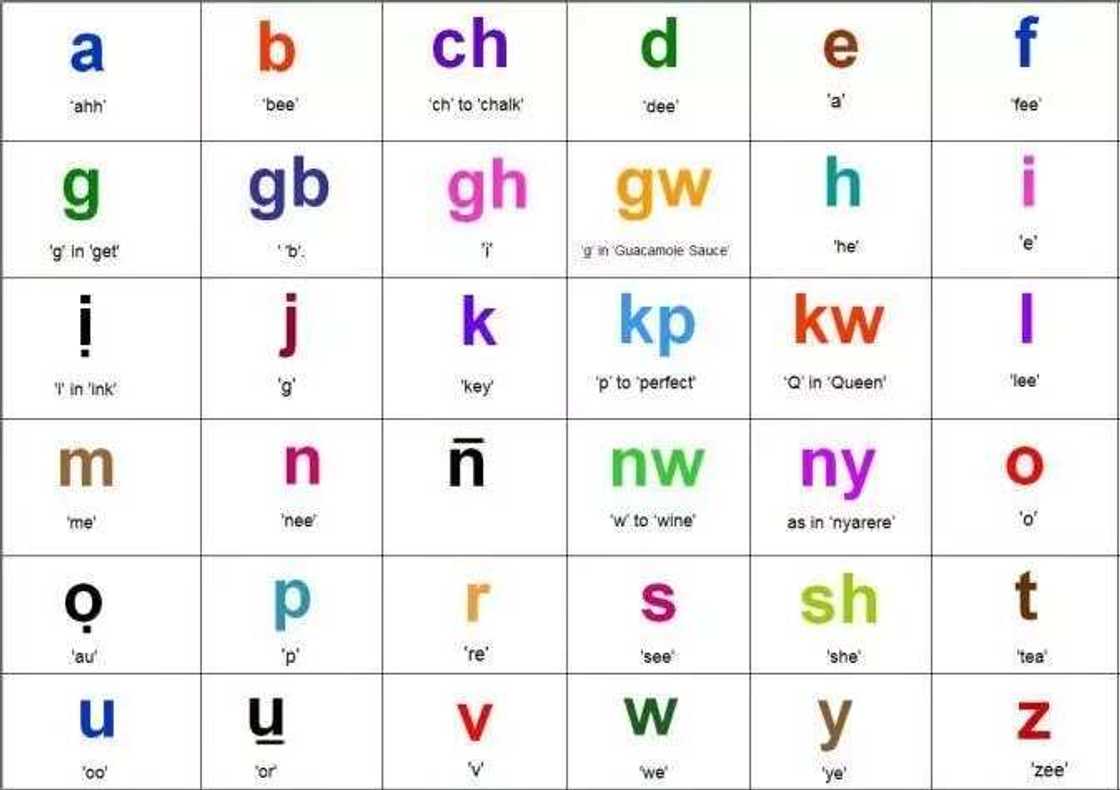
Igbo language alphabet
Igbo alphabet letters resemble a Latin alphabet but have peculiarities in pronunciation. Still, writing and teaching are provided on Latin letters basis.
Vocalism of the Igbo language includes eight vowel phonemes, which form 2 series regarding the degree of ascent: high and low. Within this opposition, a harmony of vowels is realized, analogous to the synchronism in some other languages of the group.
There are phonological contrasts of tones with both grammatical and lexical meanings. Igbo has a typical as many other languages in West Africa, the phenomenon of step-down sounds in the Syntagma. Personal pronouns in singular, form 2 series: independent pronouns and subjective brindle pronominal indicators (in plural the latter are absent). In case of the use of pronominal symbols, the vowel prefix of the verb stem is omitted (preserved with pronouns plural).
Igbo language history
READ ALSO: Origin of Igbo tribe in Nigeria
The first printed source in which individual words and expressions were officially published in the Igbo language was the book History of the Mission of the Evangelical Brothers in the Caribbean. It was in 1777.
Later in London, a story about Olaudah Equiano was published. This time about 80 words on Igbo was used. Over time, the missionaries and writers who came to Nigeria increasingly often faced the use of various dialects of Igbo. Gradually, the language was spread almost throughout eastern Nigeria.
In 1972, the SPILC introduced specific standards for the Igbo language and applied significant conditions for the language to become more prolific in other parts of the continent.
Igbo grammatical relations

Igbo language learning divides verbs into two tonal morphological classes: high and low. There are two conjugated verb forms ("times") - perfect and imperfect type, or italic and punctuation, and also three aspects. Independent and three dependent verbal forms are opposed. The latter is used for different kinds of subordinate clauses (differ in tonal characteristics). There is also a system of verbal suffixes serving to express various additional meanings, including temporary.

Names are also divided into morphological classes according to tonal schemes in different syntagmatic constructs, in particular in a genitive construction.
Writing is done on a Latin basis. Different dialects have their own written traditions, as well as various Igbo words and meanings and also there is no single literary norm. In the 1970's and 80's increasingly widespread, especially in the sphere of written use, received the standards of dialect such as Owerri.
Igbo greetings
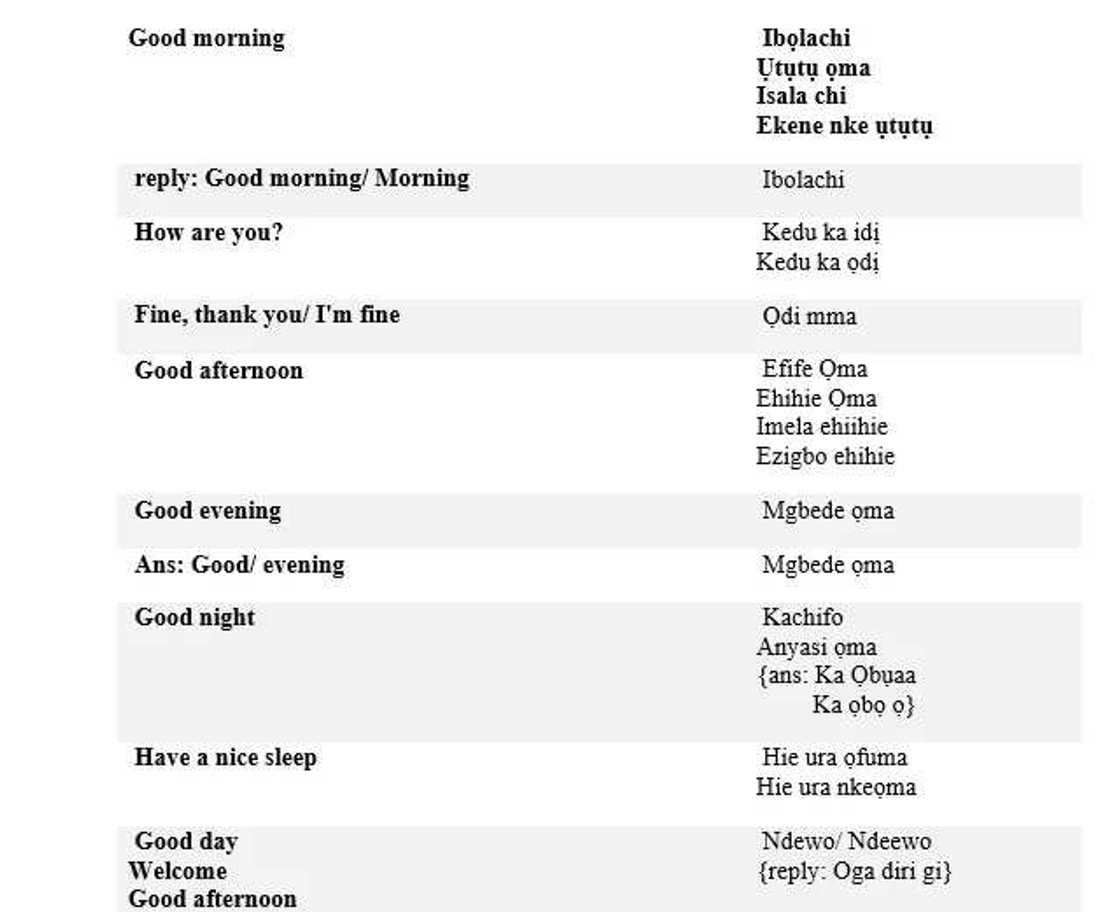
These are general ways of greetings in Igbo, still one should keep in mind, there are huge amount of local ways to address people and especially friends and family members. Though living in a specific community will easily help you tolearn the dialect in a very short time period.
Despite the fact that Igbo is studied and taught in the eastern schools of Nigeria, English remains dominant in the use of the country's literary language. Reading and writing in the Igbo language are not very widespread in Nigeria. Often Igbo is replaced by the so-called Pidgin. Nevertheless, Igbo speakers often speak freely both in Igbo and in English.
READ ALSO: Igbo schools open in United States, South Africa
Source: Legit.ng





