Types of thermometers and their uses, pictures, advantages, disadvantages
Thermometers are instruments used to measure and indicate temperature. There are multiple types of thermometers in the contemporary market. Different types are used for different reasons, for example, research, cooking, and monitoring the body temperature of patients.

Source: Original
Did you know different types of thermometers have different uses? Discover the different types in the market, their functions, pros, and cons.
Types of thermometers available today
Many, if not all, of us have used thermometers for various reasons. Most people know those used to monitor patients' temperatures and those found in school science labs.
There are multiple thermometer types used for different reasons. The type used for cooking, for example, is different from the type used to monitor patients.
What is a thermometer?
A thermometer is a device used to detect the temperature or temperature difference (the degree of hotness or coldness) of a person or object.
The two primary components of this device are a temperature sensor and a mechanism for converting what it senses into a numerical value. Below is an exploration of the different types of thermometers and their uses.
Classification based on working principle
Thermometers are classified into two based on working principle.
- Empirical thermometers: These rely on the constitutive relation between pressure, volume and temperature of the thermometric material, e.g., mercury expands when heated.
- Absolute thermometers: These measure temperature based on the theoretical concept of absolute zero. Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature that can be achieved.
NB: Empirical thermometers do not always agree with absolute thermometers on their numerical scale readings.
Classification based on function
Thermometers come in various sizes and shapes, depending on the needs of the user. They can also be classified into two broad categories based on function.
- Clinical thermometers: These are also known as medical thermometers. They are built for clinical use and are used to determine body temperature.
- Laboratory thermometers: These are used to monitor temperatures other than body temperatures. Lab thermometers are commonly used to measure boiling points, freezing points, and the temperatures of different objects in labs and testing.
Different types of clinical thermometers
There are multiple types of medical thermometers in the world. Let us look at the different types and their uses.
Regular digital thermometer
Source: UGC
A regular digital thermometer uses a heat sensor. It has a smart electronic circuit and a display screen for showing measurements.
It can be used to take readings from under the tongue or armpit. This device is considered to be the most accurate of all types of clinical thermometers.
Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Easy to use
- Accurate
- Easy to maintain
Disadvantages
- Prone to damage if dropped
- Battery power runs out often
Mercury thermometer

Source: UGC
A mercury thermometer has a glass tube filled with mercury. A standard temperature scale is marked on the tube. With the temperature changes, the mercury expands and contracts, and the temperature can be read from the scale.
When asked to draw a diagram of a thermometer, many people draw the mercury type because they have come across it at home or school.
This device can be used in homes, schools, and even industries because it determines body, liquid, and vapour temperature. It can be used to measure a baby's body temperature, in wineries and distilleries, in baking and candy making, and in power plants and piping.
Advantages
- Measure even high temperatures
- Fast response time
- More durable than alcohol thermometer because mercury does not evaporate easily
- Mercury expands linearly and less than alcohol and any other liquid
Disadvantages
- If the bulb cracks and mercury spills out, it is extremely dangerous to humans and the environment.
- Unable to detect frigid temperatures
- Low thermal coefficient
Plastic strip thermometer/ Forehead thermometer strips
This device is the least invasive and disruptive way to take a child's temperature. You hold the strip on the forehead until the colour registers along the strip. Note that it may not produce precise temperature readings.
Advantages
- Non-invasive
- Cheap
- Easy to use
Disadvantage
- Often inaccurate
Pacifier thermometer
This device looks like a baby's pacifier. It is primarily used to take body temperature of babies who are at least three months old.
To use one, give it to a baby as you would a pacifier and wait for the reading. For this, the child needs to be calm, which is challenging.
Advantages
- Easy to use
- Relatively affordable
Disadvantages
- More than three minutes needed to reach a steady state
- Often inaccurate, especially if the baby is not calm
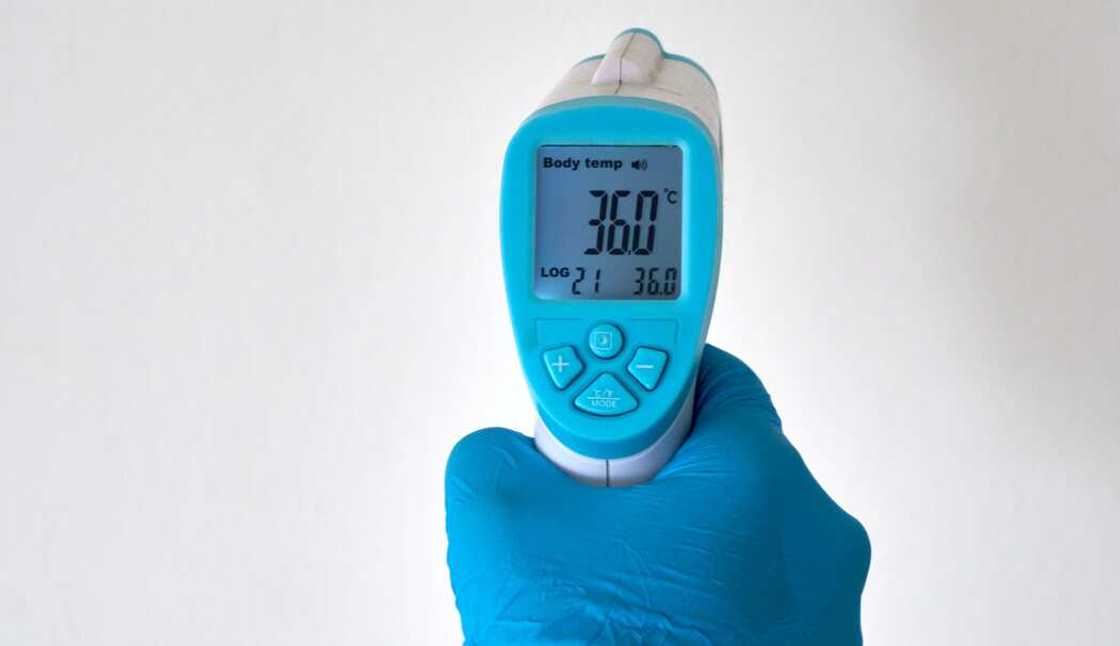
Forehead/ temporal thermometer
Source: UGC
Forehead thermometers became quite popular during the COVID-19 period. They use infrared technology to read heat and are preferred because they are a quick and sterile way to assess an individual's temperature.
They have infrared sensors that measure the temperature of the superficial temporal artery. They are commonly used in airports, malls, and stadiums to gauge people’s temperatures.
Advantages
- Non-intrusive
- Easy to use
- Fast response
- Does not require any body contact to conduct measurement
- Light in weight and compact in size
Disadvantages
- Supports short range, so the device needs to be close while taking measurement
- Accuracy of measurement varies with different models
- Infrared waves affect the eyes at high power
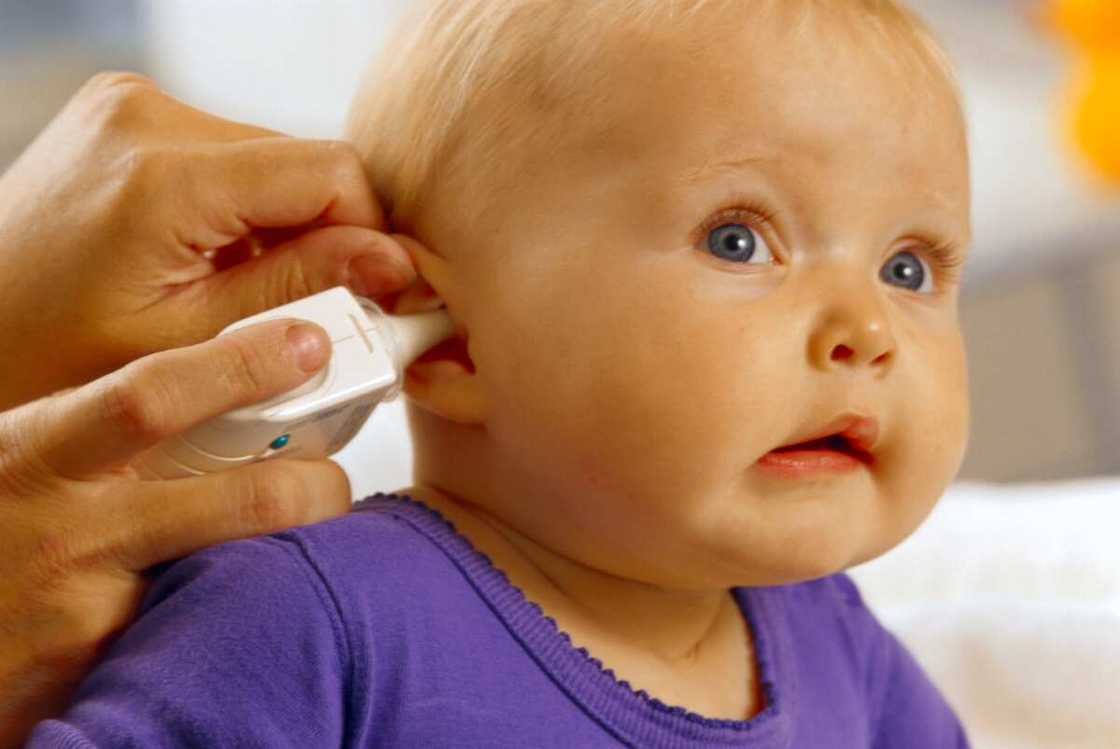
Electronic ear/ tympanic thermometer
Source: Getty Images
An electronic ear thermometer uses infrared technology to determine body temperature from inside the ear canal. It is also called tympanic because it uses the tympanic membrane within the ear to measure temperature.
Advantages
- Easy to use
- Fast response
Disadvantages
- Expensive device
- Not accurate if not properly put in the ear or if there is too much wax inside the ear
- May not fit properly in a small or curved ear canal
Different types of laboratory thermometers
Lab thermometers typically have a temperature range of -10 to 110° C. They are used in industries and science labs to measure boiling and freezing points. Below are the types of thermometers in physics, chemistry, biology, and industrial labs.
Liquid-in-glass thermometer

Source: UGC
A liquid-in-glass thermometer is made with a sealed glass containing a liquid, usually mercury or red alcohol. The volume of the liquid fluctuates as the temperature rises or falls.
As the temperature rises, the liquid expands and rises in response. It is commonly used in high school labs.
Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Easy to use
- Best suited for places with electrical problems
Disadvantages
- Fragile (prone to breakage)
- Can only be used where the liquid column is visible
- Cannot be read from a distance
- Unsuitable for high-temperature measurements
Pyrometer
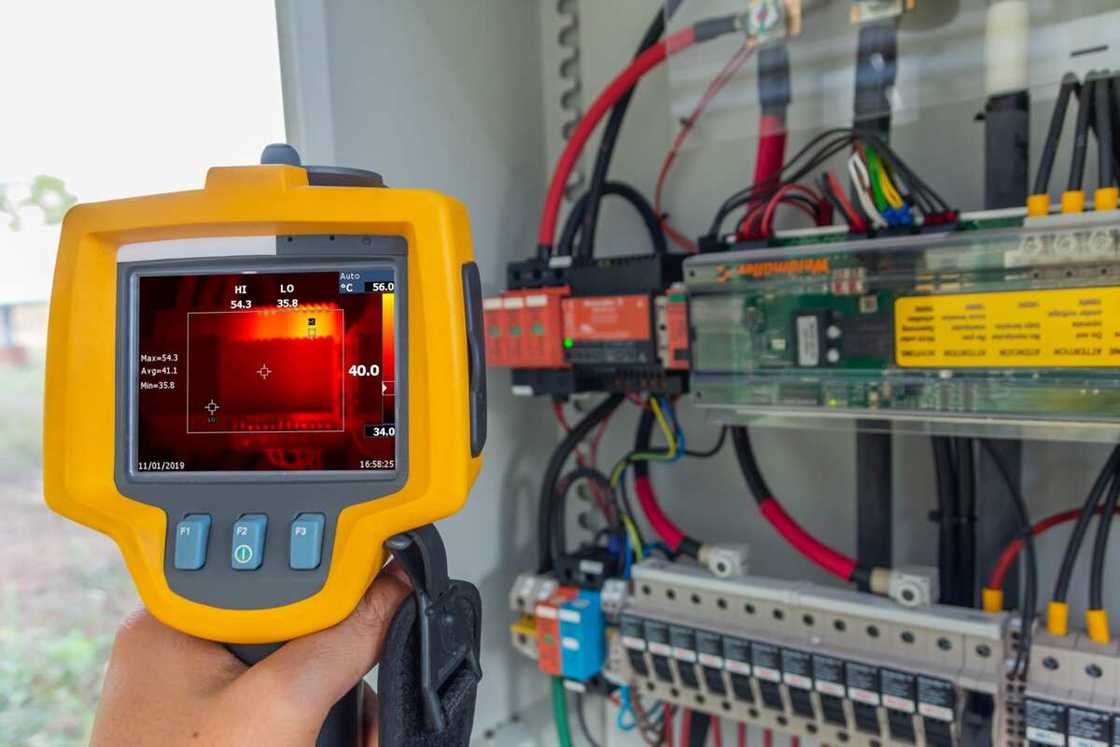

Source: Getty Images
A pyrometer is a remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of distant objects. The temperature of the object is determined by the thermal radiation the device emits.
Pyrometers are used to measure temperatures above 2000° C. They are used by industries to gauge the temperatures of objects that cannot be touched due to their intricate structure or high temperatures.
Advantages
- Non-contact and non-intrusive
- Measures extremely high temperature
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Exhibit less sensitivity at low temperatures
- Cannot be used in the continuous measurement of temperature
Bimetallic strip thermometer

Source: Getty Images
The bimetallic strip is one of the most trouble-free and durable thermometers. It has two strips of different metals bonded together and held at one end.
When heated, the metallic strips expand at different rates. This results in a bending effect that is used to measure the temperature change.
This device is commonly used in residential devices, e.g., ovens and air conditioners. It is also used in industrial devices, e.g. refineries, heaters, and hot wires.
Advantages
- Suitable for wide temperature ranges
- Easy installation and maintenance
- Fully mechanical, so no power source is needed to operate
- Less expensive than other thermometers
Disadvantages
- Not ideal for extremely high temperatures
- Calibration is disturbed if roughly handled
- May require frequent calibration
Platinum resistance thermometer
This device is used to measure the temperature over the range of 200°C to1200°C. A platinum resistance thermometer uses platinum to determine the temperature.
It operates on the principle that the resistance of platinum changes with a change in temperature. The resistance of platinum increases linearly with the temperature.
When current passes through the platinum, voltage is induced across the metal, which is measured through the voltmeter. The reading of voltage is converted into the temperature using the calibration equation.
It is commonly used to give the highest accuracy for routine industrial work, e.g., to measure the temperature in nuclear reactors.
Advantages
- High accuracy of measurement
- Measures a wide range of temperature
Disadvantages
- Pricey
- Requires additional equipment such as bridge circuit
Thermocouple thermometer/ thermal junction/ thermel

Source: Getty Images
A thermocouple is a sensor for measuring temperature. This sensor consists of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end. These wires are connected to a thermocouple.
Unlike the bimetallic strip thermometer, two different metals are used. A thermocouple can provide temperature measurements over a wide range of temperatures.
This device is commonly used in oven control, clean-in-place sensors, food chain monitoring, hotplate control and monitoring, and steam kettle temperature control.
Advantages
- Can be used at very high temperatures
- Can be used in demanding environments
- High reproducibility
- Fast response time
- Accurate at a wide operating range
Disadvantages
- Susceptible to drift over time
- Vulnerable to corrosion if not well-insulated
- Signals are not perfectly linear
Probe thermometer
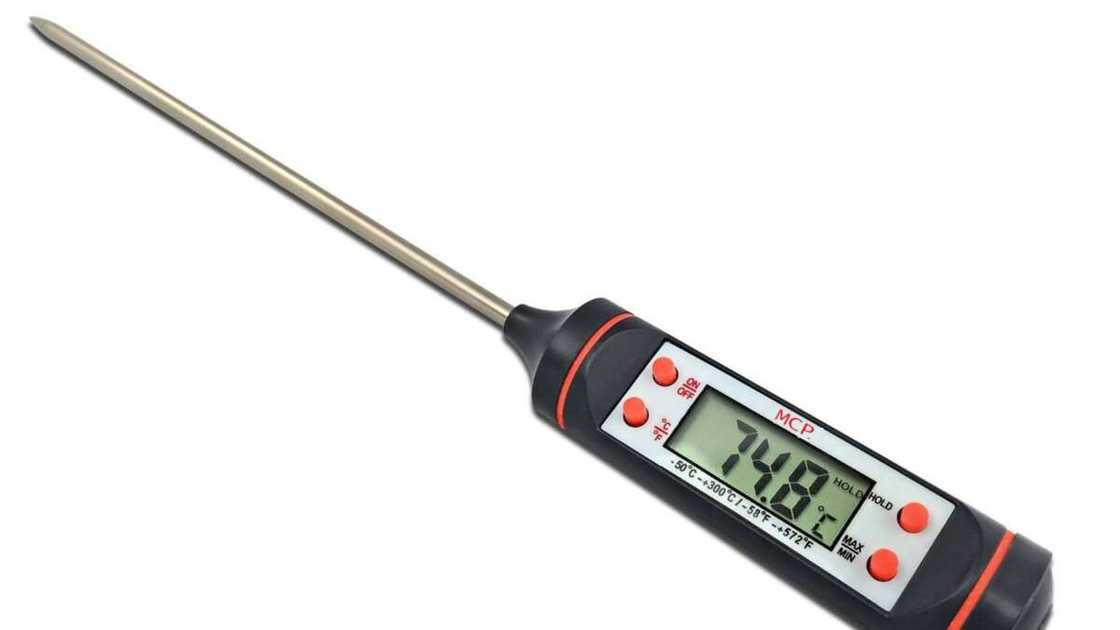

Source: UGC
A probe thermometer is a device with a pointy metal stem that can be inserted into food. It is used to ensure proper internal food temperatures are reached and maintained to avoid food-borne illnesses, e.g., roasting meat and baking.
Advantages
- Fast response time
- Higher accuracy than traditional thermometers
Disadvantages
- Relatively pricey
- Not as accurate readings as digital thermometers because the forehead surface does not exactly match internal body temperature.

Read also
"They are planning to sell fuel for N720 per litre": Political analyst lambasts Atiku, Peter Obi
What is the definition of a thermometer?
A thermometer is an instrument for measuring the temperature of a system. This device is used in manufacturing, scientific research, and medical practice.
What are the 3 main types of thermometers for food?
The main types are thermocouple, thermistor, and oven cord-thermometers. These are safe for home and industrial food processing.
What are the different types of thermometers?
Classified by function, there are medical and laboratory thermometers. Each category has various options, as explored above.
There are multiple types of thermometers used in clinical, home, school, and industrial settings. A basic understanding of the various types will help you choose an appropriate device for your needs.
Legit.ng recently published interesting facts about Orthodox churches in Nigeria. The Orthodox mission in the country began as an ethnic need for the hundreds of Greek and Cypriot immigrants who had relocated there.
The first Orthodox church in Nigeria was built decades before the colonial era. The mission has since expanded and has many churches spread across the country.
Source: Legit.ng

Cyprine Apindi (Lifestyle writer) Cyprine Apindi is a content creator and educator with over six years of experience. She holds a Diploma in Mass Communication and a Bachelor’s degree in Nutrition and Dietetics from Kenyatta University. Cyprine joined Briefly.co.za in mid-2021, covering multiple topics, including finance, entertainment, sports, and lifestyle. In 2023, she finished the AFP course on Digital Investigation Techniques. She received the 2023 Writer of the Year Award. In 2024, she completed the Google News Initiative course. Email: cyprineapindi@gmail.com

Adrianna Simwa (Lifestyle writer) Adrianna Simwa is a content writer at Legit.ng where she has worked since mid-2022. She has written for many periodicals on a variety of subjects, including news, celebrities, and lifestyle, for more than three years. She has worked for The Hoth, The Standard Group and Triple P Media. Adrianna graduated from Nairobi University with a Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) in 2020. In 2023, Simwa finished the AFP course on Digital Investigation Techniques. You can reach her through her email: adriannasimwa@gmail.com